Pharmacokinetics: How Your Body Processes Medications
When you take a pill, it doesn’t just sit there and work—it goes on a journey through your body. This journey is called pharmacokinetics, the study of how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and eliminates drugs. Also known as ADME, it’s the science behind why some pills kick in fast, others last all day, and why certain drugs can’t be taken with grapefruit. Without understanding pharmacokinetics, you’re guessing how your meds work—and that’s risky.
It starts with absorption, how the drug enters your bloodstream. A pill swallowed on an empty stomach might hit your blood faster than one taken after a big meal. Then comes distribution, how the drug travels to where it’s needed. Some drugs bind to proteins in your blood and can’t reach their target until they’re freed up. Others cross the blood-brain barrier and affect your brain—like antidepressants or sleep aids. Next is drug metabolism, how your liver breaks down the medicine. This is where genes matter. If you have a slow CYP2D6 enzyme, you might process drugs like antidepressants or painkillers differently than someone else. That’s why genetic testing for drug metabolism can help avoid side effects. Finally, elimination, how your kidneys or liver flush out the leftovers, determines how often you need to take a dose. If your kidneys aren’t working well, a drug can build up to dangerous levels.
Pharmacokinetics explains why switching to generics sometimes causes issues, why some drugs interact with grapefruit, and why certain medications need blood tests to stay safe. It’s the hidden reason behind dosage changes, timing of pills, and why some people feel side effects while others don’t. The posts below dive into real cases—like how clozapine monitoring changed in 2025, why bepotastine eye drops work faster than pills for allergies, or how grapefruit messes with cholesterol meds. You’ll see how pharmacokinetics connects to every drug you take, whether it’s for sleep, blood pressure, depression, or pain. No jargon. No fluff. Just clear, practical insights that help you understand what’s really happening inside your body when you swallow a pill.
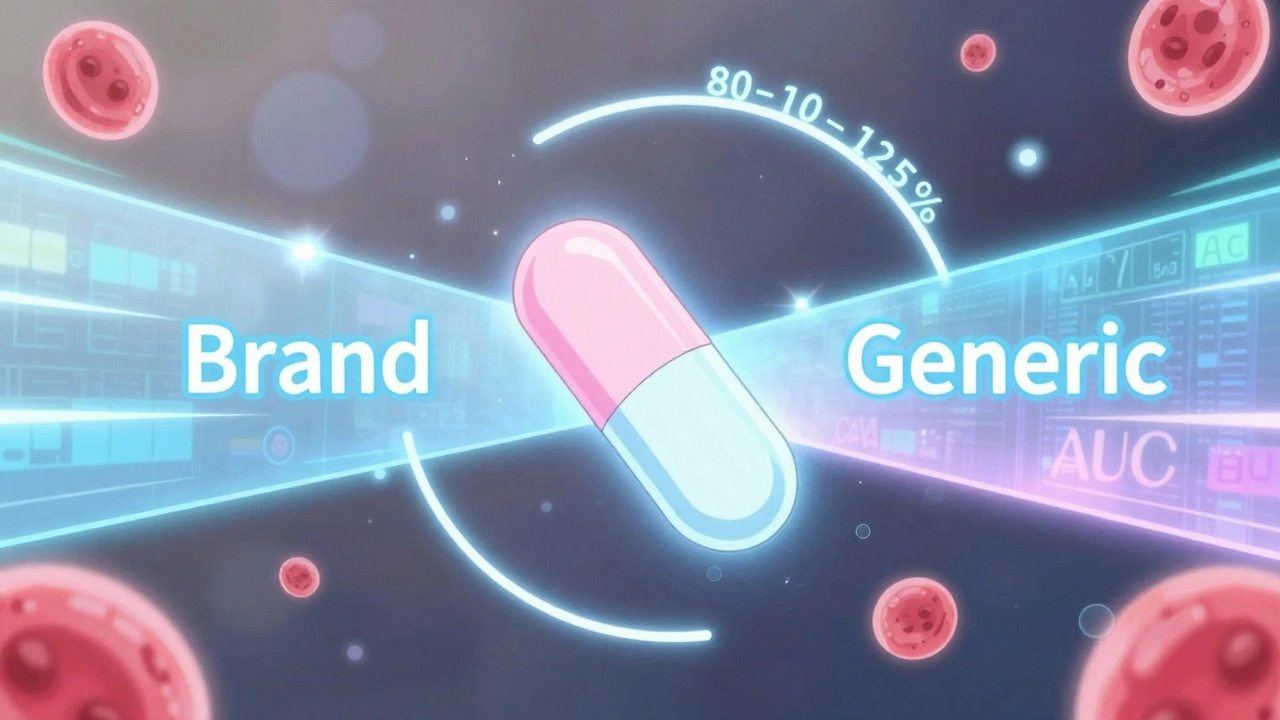
The 80-125% Rule: Understanding Bioequivalence Confidence Intervals for Generic Drugs
The 80-125% rule ensures generic drugs are absorbed the same way as brand-name versions. It's based on pharmacokinetic data, not drug content, and is used globally to approve safe, affordable generics.
December 1 2025