Understanding Tattoos and the Skin
Before delving into the relationship between skin infections and tattoos, it's crucial to understand the basics of tattoos and our skin. Tattoos are a form of body modification that involves injecting ink into the dermis layer of the skin to create a design. This process causes a wound in the skin, which is susceptible to infection if not properly cared for. Our skin, the largest organ in our body, has a primary role to protect us from harmful elements, including bacteria and viruses. When the skin's barrier is broken, like when getting a tattoo, it can leave the body vulnerable to infections.
The Connection Between Tattoos and Skin Infections
Getting a tattoo involves breaking the skin's surface, which provides a potential entry point for bacteria. If the tattoo equipment is not sterilized properly, harmful bacteria can be introduced into the body, leading to potential skin infections. Moreover, if the aftercare instructions are not followed correctly, this risk is further increased. But it's important to remember that not every tattoo will result in a skin infection. The risk depends on many factors, including the hygiene standards of the tattoo parlour, the aftercare, and the individual's overall health.
Common Types of Skin Infections From Tattoos
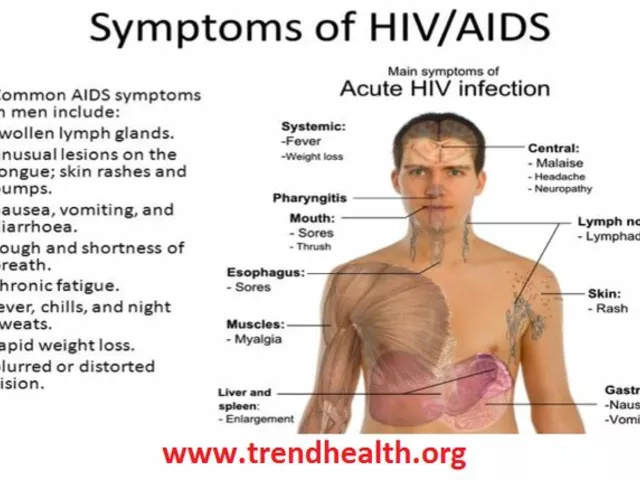
There are several types of skin infections that can occur after getting a tattoo. These include bacterial infections, viral infections, and fungal infections. Bacterial infections are the most common and typically occur shortly after getting the tattoo. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and pus. Viral infections, while less common, can be serious and may include diseases like Hepatitis B and C. Lastly, fungal infections are rare but can happen if the tattooed area is not kept clean and dry.
Recognizing the Signs of a Skin Infection
Identifying a skin infection early on is crucial to avoid any complications. Some common signs of a skin infection include redness, swelling, warmth or heat over the tattooed area, pus, and fever. The tattooed area may also be painful to touch. If you notice any of these symptoms, it's important to seek medical attention immediately.
Preventing Skin Infections After Tattoo
The best way to prevent skin infections after getting a tattoo is through proper aftercare. This includes cleaning the area gently with mild soap and water, applying a thin layer of antibiotic ointment, and avoiding sun exposure. It's also important to avoid soaking the tattoo in water for the first few weeks and to keep it clean and dry. Additionally, ensure that your tattoo artist uses sterilized equipment and follows all necessary hygiene protocols.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you notice any signs of infection, it's important to seek medical attention immediately. This is particularly crucial if you have a high fever, severe pain, or if the infection seems to be spreading. A healthcare professional can help diagnose the infection and provide appropriate treatment, which may include antibiotics.
Treating Skin Infections From Tattoos
Treatment for skin infections from tattoos will depend on the type and severity of the infection. Mild bacterial infections can often be treated with topical antibiotics. More severe infections may require oral antibiotics or even hospitalization. It's important to follow all treatment instructions and to complete the full course of antibiotics if prescribed.
Long-term Risks and Complications
While most skin infections can be treated effectively, there can be long-term risks and complications if left untreated. These can include scarring, changes in skin color, and even systemic infections that can affect other parts of the body. In severe cases, untreated skin infections can lead to serious health problems such as sepsis, which is a life-threatening condition.
Conclusion: The Importance of Choosing a Reputable Tattoo Parlor
While the risk of skin infections from tattoos is real, it can be significantly reduced by choosing a reputable tattoo parlor. A good tattoo artist will maintain high hygiene standards, use sterile equipment, and provide clear aftercare instructions. The decision to get a tattoo should not be taken lightly, and it's crucial to be informed about the potential risks and how to prevent them.

Gary Smith
July 6, 2023 AT 17:48America's ink standards are a disgrace!!!
Dominic Dale
July 9, 2023 AT 01:21The tattoo industry, as you may have guessed, is a hotbed of hidden agendas that the mainstream media refuses to expose.
Every needle that pierces your dermis is potentially a conduit for micro‑chips designed to monitor your biometric data.
While reputable parlors claim they sterilize their tools, the reality is that many use the same containers of diluted bleach for weeks, creating a breeding ground for antibiotic‑resistant bacteria.
These pathogens, once introduced, can hitch a ride on the very ink that you paid good money for, effectively turning your artwork into a silent Trojan horse.
What the public doesn't see is the subtle partnership between certain tattoo supply manufacturers and shadowy biotech firms eager to test experimental viral vectors on unsuspecting clients.
The after‑care ointments, marketed as soothing balms, often contain undisclosed immunosuppressants that delay the body's natural response to infection.
If you notice a swollen, warm patch around your fresh ink, it might not be a simple bacterial infection but a sign that your immune system is being deliberately dampened.
Moreover, the proliferation of Instagram‑driven hype has led to a surge in pop‑up shops that operate without any oversight, turning entire neighborhoods into breeding zones for exotic fungal spores.
These spores, unlike the usual Staphylococcus aureus, can remain dormant for months, only to erupt when your skin finally relaxes after the initial healing phase.
Compounding the problem, many municipal health departments lack the funding to inspect these transient studios, leaving the public to fend for themselves.
The CDC's guidelines, while comprehensive on paper, are rarely enforced, creating a regulatory vacuum that profiteers happily exploit.
If you think that a simple fever after a tattoo is harmless, consider that viral hepatitis B and C have been traced back to contaminated ink batches sourced from offshore labs.
These labs, operating under the radar, often cut corners by using animal‑derived pigments that can harbor zoonotic agents.
In short, your skin's barrier is not the only thing being breached; your personal data, health, and even your future autonomy are at stake.
The only real protection is to demand full transparency, refuse to trust anonymous suppliers, and seek out parlors that publish third‑party sterilization certificates for every single session.
christopher werner
July 11, 2023 AT 08:54Thanks for laying out the complexities in such detail. I appreciate the caution but also recognize that many artists take their hygiene seriously. Balancing vigilance with realistic expectations can help newcomers stay safe without falling into paranoia. Ultimately, informed aftercare remains the most practical defense.
Matthew Holmes
July 13, 2023 AT 16:28Imagine the ink seeping deep, whispering secrets to the skin.
A single drop of contamination can turn a masterpiece into a nightmare.
We must heed the silent warning signs before they scream.
Patrick Price
July 16, 2023 AT 00:01i cant beleive some studios skip sterial steps they tought it woudnt matter but it does
Travis Evans
July 18, 2023 AT 07:34Yo, if you're getting inked, treat that spot like a new plant-water it gently, keep the sun off, and watch it grow without weeds.
A little patience and clean hands go a long way, trust me.
Your art will stay fresh and vibrant.
Jessica Hakizimana
July 20, 2023 AT 15:08Every tattoo is a story etched onto the canvas of our lives, and like any good story, it deserves careful nurturing.
When you honor the after‑care routine, you're honoring the narrative itself, allowing it to unfold beautifully over time.
Stay positive, stay clean, and let your skin sing.
peter derks
July 22, 2023 AT 22:41Hey folks, remember that the best after‑care routine is a combo of simple steps and a positive mindset.
Wash with mild soap, pat dry, and keep that fresh ink moisturized-your body will thank you.
Sarah DeMaranville
July 25, 2023 AT 06:14Honestly most of this is overblown.
Edward Leger
July 27, 2023 AT 13:48Contemplating the skin as both barrier and narrative medium invites a measured approach to its care.
Thoughtful aftercare honors both its protective function and its role as personal expression.
Keyla Garcia
July 29, 2023 AT 21:21Wow, look at all the drama over a little ink 😱🙄 If you can't even follow a simple ointment rule, you deserve whatever infection you get 😂💀
Ismaeel Ishaaq
August 1, 2023 AT 04:54Listen up-if you want that tattoo to stay a masterpiece, you gotta treat it like a championship belt, no excuses!
Scrub it, guard it, and keep the haters talkin' while you rock that flawless art.
Jesse Goodman
August 3, 2023 AT 12:28Good hygiene wins 🛡️